Reemployment Prospects Vary by Gender, Race and Hispanic Ethnicity
The June 2020 Update on How COVID-19’s Job Disruptions Vary by Gender, Race and Hispanic Ethnicity
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted the work of many U.S. workers and these effects are unequally distributed. This post looks at how those job disruptions have affected key groups, based on the June 2020 jobs report (that is, the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Employment Situation news release).
Male and white workers continue to fare better than female, African American, Asian and Hispanic workers. By faring better, I mean both that fewer jobs have been disrupted and/or that more workers whose jobs have been disrupted retain a tie to an employer. Compared to a permanent layoff, a disruption that does not cut the tie between worker and employer has the potential to be reversed much more easily.
Background
In April, I published a post about the monthly jobs reports and some indicators that measure job disruptions from COVID-19. By “job disruptions,” I mean any of the six ways that a worker’s labor market status might be affected by the pandemic—see the next section. I apply that approach to analyze the jobs reports for April, May and June. It may be helpful to read those posts as background. I present results by sex, race and ethnicity as for May in this post.
Six distinct ways the crisis has disrupted (suspended or curtailed) U.S. jobs
Since disruptions can take many forms, I track these indicators in the attached COVID-19 job disruption table:
- Employed workers not at work—workers on leave from their employer, whether paid or not (for illness, family reasons, vacation, etc. The bureau believes that many of these workers are actually on temporary layoff. See questions 7-14 of this note and my misclassification post for more on this topic. By including them here, we construct a measure that is unaffected by the degree of misclassification.
- Workers part-time for economic reasons—workers who prefer to work full-time, but only found a part-time job or who usually work full-time, and who also had their hours reduced by their employers.
- Unemployed workers on temporary layoff (furloughed)—laid-off workers who expect a recall.
- Unemployed workers not on temporary layoff—includes workers permanently laid off, new workers, re-entrants and job leavers.
- People out of the labor force who currently want a job—people without a job who are not looking for work, but say they want a job.
- People out of the labor force who do not want a job—mostly students, retirees and people with disabilities or caring for family members.
For each category, I estimate the net number disrupted simply by the change in the number of workers since February. To get the overall share of workers’ jobs disrupted, I divide the sum of the job disruption types by the size of the labor force in February. So, the share would be close to zero if few workers moved into these states. And, it would be close to 100 percent of all workers had entered into one of these states since February. The first three types of disruptions maintain workers’ relationships with an employer, in contrast to the latter three. See here for why having a tie to your employer matters.
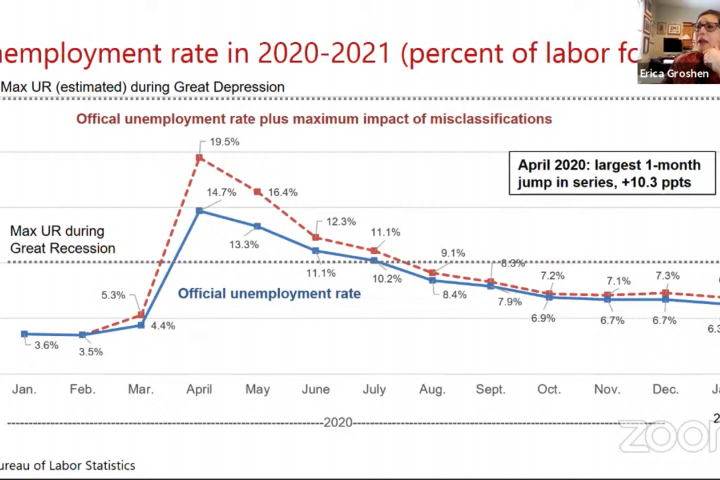
Share of workers with jobs disrupted in June
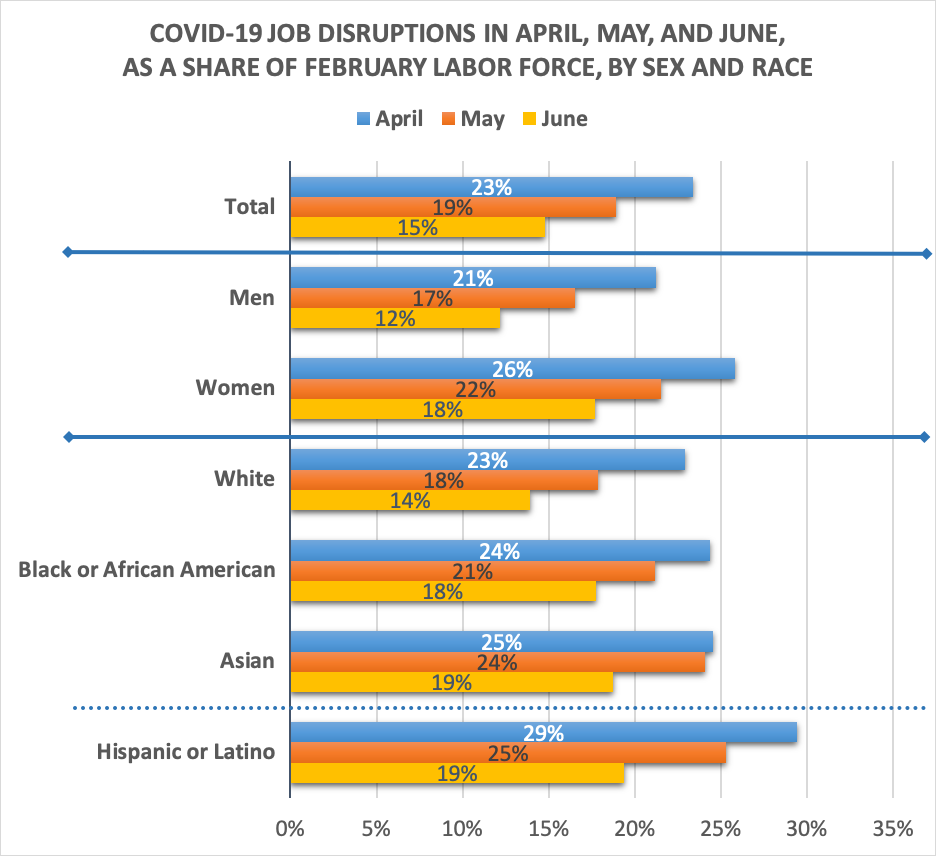
The table presents counts of the jobs disrupted in these six ways, for June compared to February. The total disrupted appear below the six types, both in number of workers and as a share of the labor force in February. The first column shows totals for all U.S. workers, while the others break up the total by gender and then by race and Hispanic ethnicity. The bars in Figure A show the share of the labor force with disrupted jobs in April, May and June. Note that I do not have standard errors for these estimates. The smaller differences, particularly for the smaller population segments, may be due to sampling error, so they will bear watching for their persistence.
- The bottom bars of Figure A show that in June COVID-19 disrupted the jobs of 15 percent of the U.S. labor force, a substantial decrease from the 23 percent of jobs disrupted in April.
- The next sets of bars in Figure A repeat the exercise separately for men and women. Women’s jobs were more disrupted by COVID-19 than men’s jobs in all three months. Although both genders showed improvement in June, the gap did not narrow.
- Continuing down Figure A, jobs held by white workers have been less disrupted than jobs held by African American, Asian or Hispanic workers. And, white workers saw more improvement from April to June than the other groups.
- African American workers had a higher share of their jobs disrupted in all three months than did white workers. Along with high death rates from COVID-19, African Americans have seen dire labor market impacts from COVID-19.
- Asian and Hispanic workers also have more disruptions than white workers and have converged to similar rates as African American workers as of June.
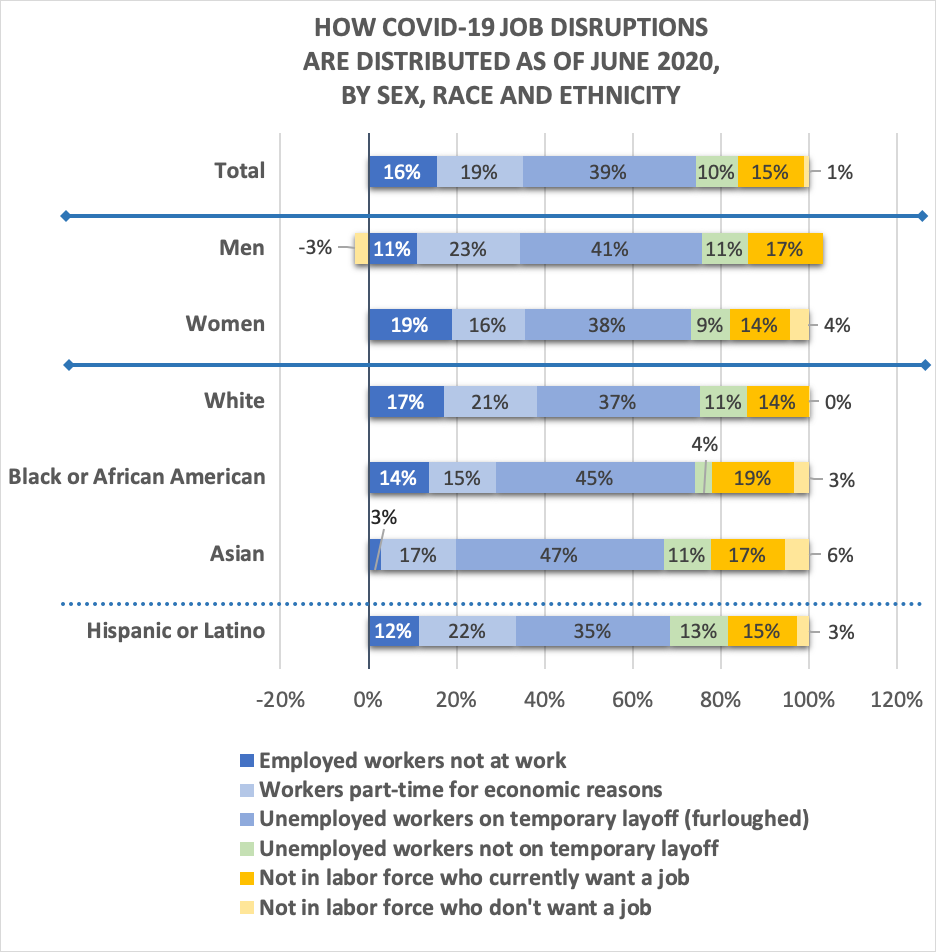
Type of disruptions as of June
Figure B shows how each group’s job disruptions are distributed. The percentages shown also appear below the counts of workers in the table (in parentheses), that is, each type’s disruption as a share of all disruptions for the group. The disruptions that preserve the relationship between worker and employer are shown in shades of blue in Figure B. The other segments represent workers who will need new jobs to be reemployed.
- Overall, 74 percent of disrupted workers still retain a tie to their employers.
- The distributions of disruptions do not vary strongly among the groups shown here. What differences we see suggest that white workers and males have fared better than the other groups.
- As of June, more men whose jobs were disrupted were still working at reduced hours (23 percent compared to 16 percent for women), so they were still earning some income. Also, more women out of the labor force than men said they did not want a job in June, possibly in order to care for children or other family members.
- Compared to white workers, the share of African American workers retaining a tie to employers is similar (74 percent versus 75 percent). However, white workers were much more likely to be still on the job, working short hours (21 percent versus 15 percent for African American workers). The share of disrupted African American workers who want a job, but who have not actively looked for work yet, is the highest of all the demographic groups. This suggests the presence of continuing barriers to job searches for this group.
- Asian and Hispanic workers have the lowest share of disruptions that preserve ties with employers (67 percent and 69 percent, respectively), suggesting more struggles for reemployment ahead.
Summary
Despite two months of rebound, U.S. job market conditions remain dire. What varies most among the groups examined here is the scale of disruption. While all groups have very large job disruptions, male workers have had fewer disruptions than women and white workers have had fewer disruptions than African American, Asian or Hispanic workers. As of June, the types of job disruptions look fairly similar across groups, but do suggest that white workers retain more ties to their employers than do Asian or Hispanic workers. Hence, by these measures, reemployment prospects for Asian and Hispanic workers look worse than those for white workers.
| Total | Men | Women | White | Black or African American | Asian | Hispanic or Latino | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of job disruption | |||||||
| Employed workers not at work | 3,779 (16%) |
1,162 (11%) |
2,617 (19%) |
3,039 (17%) |
507 (14%) |
58 (3%) |
663 (12%) |
| Workers part-time for economic reasons | 4,706 (19%) |
2,456 (23%) |
2,249 (16%) |
3,714 (21%) |
561 (15%) |
337 (17%) |
1,267 (22%) |
| Unemployed workers on temporary layoff | 9,527 (39%) |
4,339 (41%) |
5,188 (38%) |
6,539 (37%) |
1,664 (45%) |
936 (47%) |
2,013 (35%) |
| Unemployed workers not on temporary layoff | 2,327 (10%) |
1,116 (11%) |
1,212 (9%) |
1,901 (11%) |
148 (4%) |
212 (11%) |
761 (13%) |
| Not in labor force who currently want a job | 3,660 (15%) |
1,775 (17%) |
1,885 (14%) |
2,453 (14%) |
683 (19%) |
334 (17%) |
892 (15%) |
| Not in labor force who don't want a job | 268 (1%) |
-323 (-3%) |
591 (4%) |
21 (0%) |
127 (3%) |
110 (6%) |
163 (3%) |
| Total disrupted | 24,267 (100%) |
10,525 (100%) |
13,742 (100%) |
17,667 (100%) |
3,690 (100%) |
1,987 (100%) |
5,759 (100%) |
| February labor force | 164,235 | 86,597 | 77,638 | 126,954 | 20,833 | 10,596 | 29,750 |
| Total disrupted as a share of February labor force | 15% | 12% | 18% | 14% | 18% | 19% | 19% |
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (Current Population Survey) and author’s calculations. Not seasonally adjusted. Note: Hispanic or Latino workers may be white, African American or Asian.
Figure A
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (Current Population Survey) and author’s calculations. Not seasonally adjusted.
Note: Hispanic or Latino workers may be white, African American or Asian.
Figure B
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (Current Population Survey) and author’s calculations. Not seasonally adjusted.
Note: Hispanic or Latino workers may be white, African American or Asian.